Permeable Paving VS Porous Paving
As urbanisation continues to intensify, the significance of effective water drainage systems becomes increasingly paramount. Two pivotal solutions that have garnered considerable attention are permeable and porous paving.
Although people frequently use them mutually, these two types of paving systems have distinct characteristics and applications. In this article, we shall elucidate the differences between permeable and porous paving, exploring their respective attributes, benefits, and suitable applications.
Introduction to Water Drainage and Urban Surfaces
Building in cities means we need to figure out how to deal with rain and stop flooding and pollution. Concrete and asphalt don’t let water soak into the ground. This makes water run off and cause damage to the environment.
To fix these problems, engineers have developed new construction materials to improve water drainage. Let’s delve into the specifics of permeable and porous paving to understand their contributions to sustainable urban development.
Understanding Permeable Paving
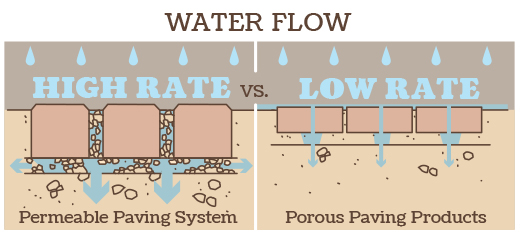
Permeable paving is when water can go through the ground instead of staying on top. Unlike traditional paving, permeable surfaces are designed with small gaps or voids to enable infiltration of water.
Components of Permeable Paving Systems
Permeable paving is made up of a top layer that lets water through, a layer of rocks underneath for support and storage, and a sub-base that helps filter water to the ground or drainage system.
Advantages of Permeable Paving
Permeable paving is good because it helps reduce water runoff, refill groundwater, and clean pollutants from water. Permeable paving helps cool urban areas by letting moisture evaporate through the surface, reducing the ‘heat island’ effect.
Exploring Porous Paving
Porous paving is a special kind of permeable paving. It’s made from materials that let water pass through them. This means that the pavement has lots of small holes that let water go through easily.
Components of Porous Paving Systems
Porous paving is like permeable paving. It has a porous top layer, a base to store water, and a bottom layer to filter water. However, the distinguishing feature of porous paving is the porous nature of the surface material itself.
Advantages of Porous Paving
Porous paving shares many of the same benefits as permeable paving, such as improved water drainage and groundwater recharge. The surface material can hold lots of water and is good for areas with lots of rain because it absorbs water well.
Permeable vs Porous Paving: Key Differences
The primary difference between permeable and porous paving lies in the design of the surface layer. Permeable paving lets water go through small spaces between pavers. Porous paving lets water go through the material itself.
Applications of Permeable and Porous Paving
Permeable paving is often used in residential and light commercial applications such as driveways, sidewalks, and parking lots. Porous paving allows water to drain more quickly and is good for busy places like commercial areas and streets.
Maintenance Considerations
Both permeable and porous paving require maintenance to ensure continued effectiveness. Regular cleaning to remove debris and prevent clogging is necessary. Porous surfaces, in particular, may require vacuum sweeping to keep the pores open.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Permeable and porous paving are eco-friendly alternatives to traditional paving methods. These systems help water soak into the ground instead of running off. This prevents floods and helps keep water moving naturally.
Reducing Urban Heat Islands
Both types of paving contribute to reducing the urban heat island effect by maintaining natural evaporation and transpiration processes. This can lead to cooler urban environments, especially during hot summer months.
Enhancing Water Quality
Permeable systems can make water cleaner by catching dirt and pollutants. This results in cleaner water entering the groundwater or municipal drainage systems.
The Role of Permeable and Porous Paving in Urban Planning
Urban planners are increasingly recognizing the value of permeable and porous paving in creating sustainable and resilient cities. By integrating these systems into urban landscapes, planners can address water management challenges while promoting environmental stewardship.
Case Studies of Successful Implementations
Several cities around the world have successfully implemented permeable and porous paving in their urban infrastructure. These case studies demonstrate the practical benefits and long-term viability of these systems.
Choosing the Right Paving Solution
When selecting a paving solution, it is important to consider the specific needs of the project. Factors such as weather, traffic, and soil type will determine the best option between permeable and porous paving.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Permeable and porous paving systems may be more expensive initially. However, they can save money in the long term. This is because they manage water more effectively and reduce environmental impact.
Regulatory Compliance
Many regions have regulations in place that encourage or mandate the use of permeable and porous paving to manage stormwater. Compliance with these regulations is an important consideration for any paving project.
Conclusion
Permeable and porous paving represent innovative solutions to the challenges of urban water management. By understanding the differences between these systems, stakeholders can make informed decisions that balance functionality, sustainability, and aesthetics.
Permeable and porous paving helps make cities more sustainable by working with nature to create stronger and more enjoyable urban areas.
In summary, permeable and porous paving are both effective strategies for managing stormwater in urban areas. The decision on which one to choose will depend on the needs of the project. Both options have environmental benefits that help create sustainable cities.
We are looking for ways to help the planet by using permeable and porous paving in cities.